COVID-19
The IMF is fully committed to supporting our member countries, particularly the most vulnerable; we have the tools to help; and we are coordinating closely with our partner institutions.

COVID-19 AND THE WAR IN UKRAINE
News & Publications
Global Economy Shakes Off Tariff Shock Amid Tech-Driven Boom
But risks are rising, including from the concentration of tech investment and the negative effects of trade disruptions, which may build over time
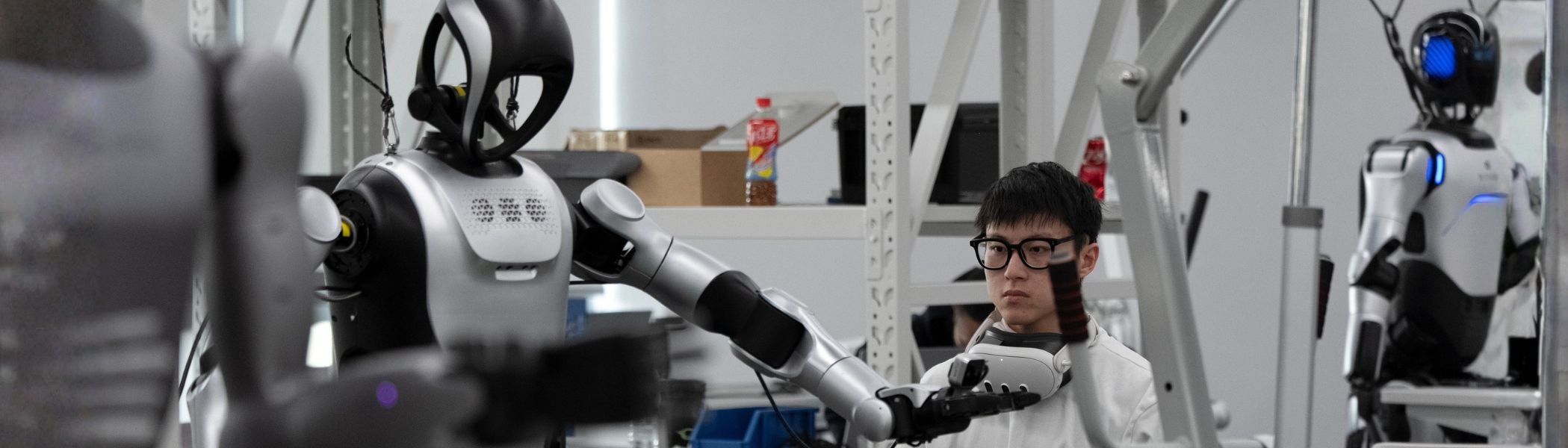
New Skills and AI Are Reshaping the Future of Work
Policy choices will determine whether workers and firms are adequately prepared for the AI revolution
Top 10 Blogs of 2025
Debt, Stablecoins, AI, and Global Economy’s New Era Drew Blog Readers
Top Five IMF Blog Charts of 2025
Chart of the Week visuals illustrate major developments during a year of uncertainty and resilience
How Stablecoins Can Improve Payments and Global Finance
New technology can foster innovation and financial inclusion, or cause fragmentation and turbulence in many countries
Better Economic Measurement Is About Wiser Use, Not Just More Data
Statistics are a means, not an end, that should serve the public by helping us see the world more clearly and make better decisions
Podcast: Navigating a More Fragile World
With shock upon shock hitting the world economy in the last three years, IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva's customary opening speech to the Annual Meetings warned of a darker global outlook and emphasized the need for the world to come together to deal with the consequences.