Special Drawing Rights

The SDR is an international reserve asset created by the IMF to supplement the official reserves of its member countries.
The SDR is not a currency. It is a potential claim on the freely usable currencies of IMF members. As such, SDRs can provide a country with liquidity.
A basket of currencies defines the SDR: the US dollar, Euro, Chinese Yuan, Japanese Yen, and the British Pound.

Factsheet: Special Drawing Rights (SDR)
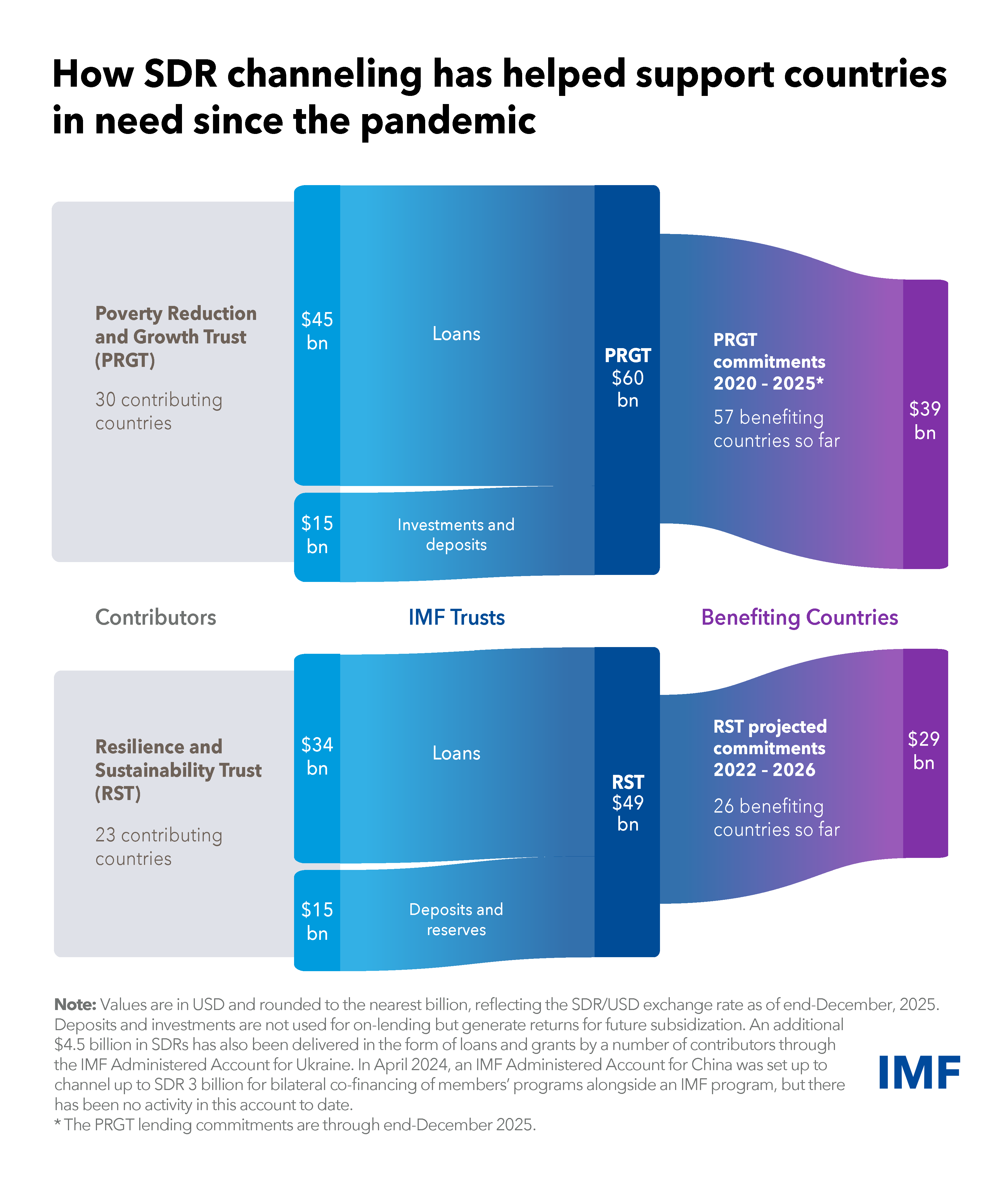
Since the onset of the pandemic, SDR channeling (and equivalent currency amounts) has helped many countries in need, especially those eligible for financial support from the IMF’s Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust (PRGT) and the Resilience and Sustainability Trust (RST).
Since 2020, SDR channeling of $60 billion has supported interest-free loans through the PRGT for our poorest members. This financing helps support growth enhancing reforms in these countries. So far, loans amounting to about $39 billion through end-December 2025 have been committed to 57 countries and could benefit more in the years ahead.
Channeling has also supported the operations of the RST, which delivers affordable long-term financing to help vulnerable countries tackle long-term challenges including climate change. To date, 23 RST partners have channeled or committed to channeling about $49 billion to the RST, which is expected to contribute toward meeting an estimated $29 billion in affordable financing.
7 Things you need to know about the SDR
IMF
Q. How many SDRs have been allocated so far?
The Fund has allocated a total of SDR 660.7 billion (equivalent to about US$935.7 billion), including four general allocations and a one-time special allocation. Specifically:
- SDR 9.3 billion was allocated in yearly installments in 1970–72.
- SDR 12.1 billion was allocated in yearly installments in 1979–81.
- SDR 161.2 billion was allocated on August 28, 2009
- A special one-time allocation of SDR 21.5 billion took effect on September 9, 2009 to correct for the fact that members that had joined the IMF after 1981 had never received an allocation (the Fourth Amendment special allocation)
- SDR 456.5 billion (equivalent to about US$650 billion) was allocated on August 23, 2021, by far the largest allocation to date
-
In addition, new members to the Fund receive an SDR allocation upon their participation in the SDR Department


