Amid the prolonged and painful pandemic, risks to global financial stability have remained contained—so far. But with economic optimism fading, and with financial vulnerabilities intensifying, this is a time for careful policy calibration. To an unprecedented degree, the world’s central banks, finance ministries, and international financial institutions have asserted—for a year and a half—policy support for economic growth. Now they must craft strategies that safely approach the next stage of monetary and fiscal policy action.
The sense of optimism that had propelled markets in the first half of the year is at risk of fading.
The world’s systemically important central banks know that any unintended consequences of their actions could put growth at risk—and could, conceivably, lead to abrupt adjustments in the world’s financial markets. Uncertainty is especially intense because of the persistent pandemic-stricken atmosphere where society confronts the challenges inherent in “the three Cs”: COVID-19, crypto, and climate change, as discussed in our latest Global Financial Stability Report.
Fading optimism
Massive monetary and fiscal policy support for the economy in 2020 and 2021 helped limit the economic contraction that began at the start of the pandemic and that—for much of this year—supported a strong economic rebound. In many advanced economies, financial conditions have eased since the initial months of the pandemic. Nonetheless, the sense of optimism that had propelled markets in the first half of the year is at risk of fading.
Investors have become increasingly worried about the economic outlook, amid ever-greater uncertainty about the strength of the recovery. Uneven vaccine access, along with the mutations of the COVID-19 virus, have led to a resurgence of infections—fueling concerns about more divergent economic prospects across countries. Inflation readings have been above expectations in many countries. And new uncertainties in some major economies have put markets on alert. Those uncertainties are triggered by financial vulnerabilities that could increase downside risks, surging commodity prices, and policy uncertainty.
The deterioration in market sentiment since the April 2021 Global Financial Stability Report resulted in a significant decline in global long-term nominal yields in the summer, driven by falling real rates, reflecting concerns about long-term-growth prospects. In late September, however, investor anxiety about inflationary pressures pushed yields higher as price pressures then started to be seen as potentially more persistent than initially anticipated in some countries—entirely reversing the earlier declines.
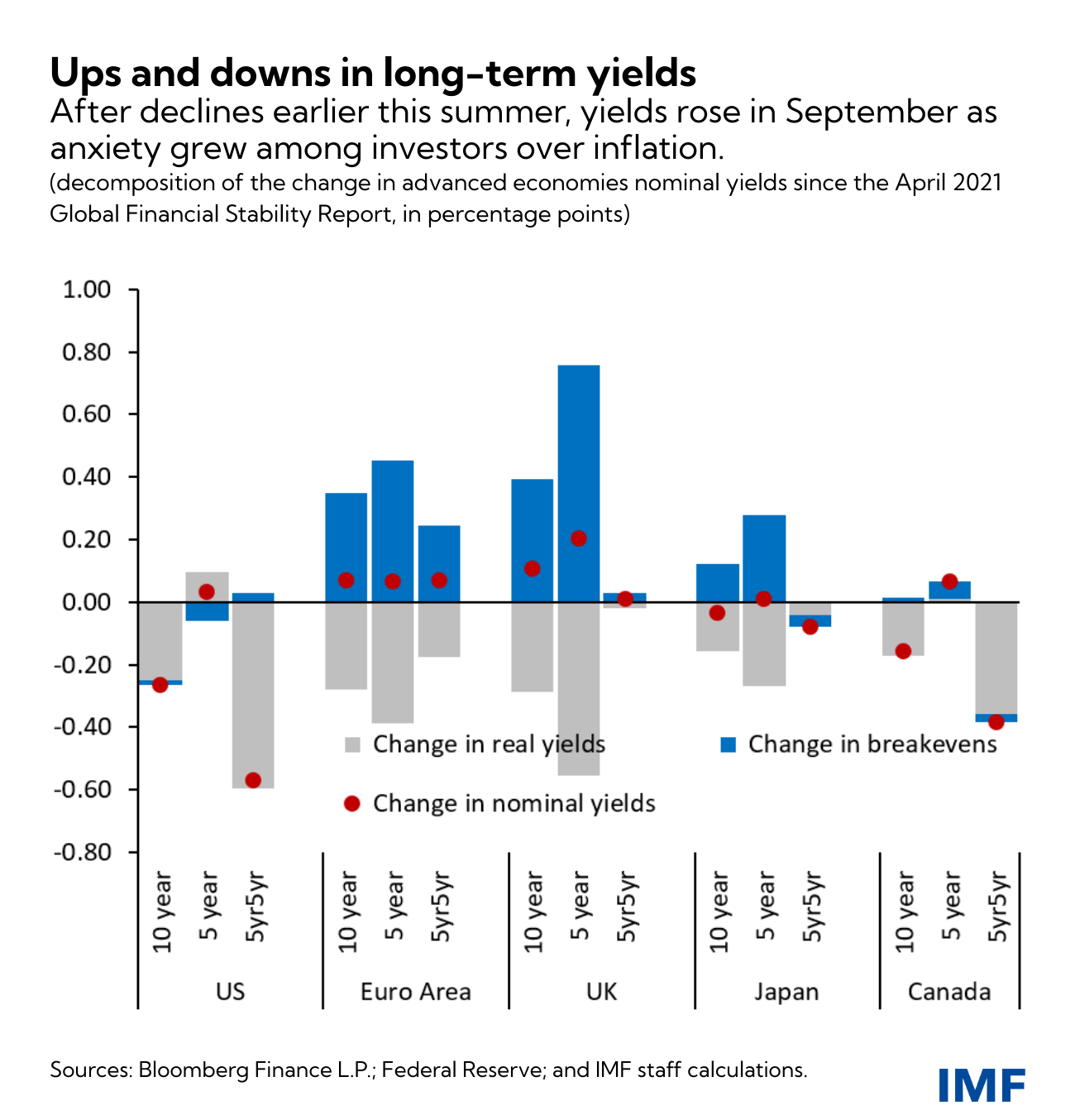
If investors, at some point, reassess abruptly the economic and policy outlook, financial markets could endure a sudden repricing of risk—and that repricing, if sustained, could interact with underlying vulnerabilities, leading to a tightening of financial conditions. This could put economic growth at risk.
Risks also bear close monitoring in other key areas. Crypto asset markets are growing rapidly and crypto asset prices remain highly volatile. Financial stability risks are not yet systemic in the crypto ecosystem, but risks should be closely monitored, given the global monetary implications and the inadequate operational and regulatory frameworks in most jurisdictions—especially in emerging market and developing economies. Likewise, as the world continues to seek ways to speed up the transition to a low-greenhouse-gas economy in order to avoid the negative economic and financial stability outcomes associated with climate change, a promising opportunity is emerging in the financial sector. While assets under management in climate-themed investment funds remain relatively small, inflows have surged, and there is a promise of cheaper funding costs for climate-friendly firms, as well as greater climate stewardship by funds.
A not-so-easy trade-off
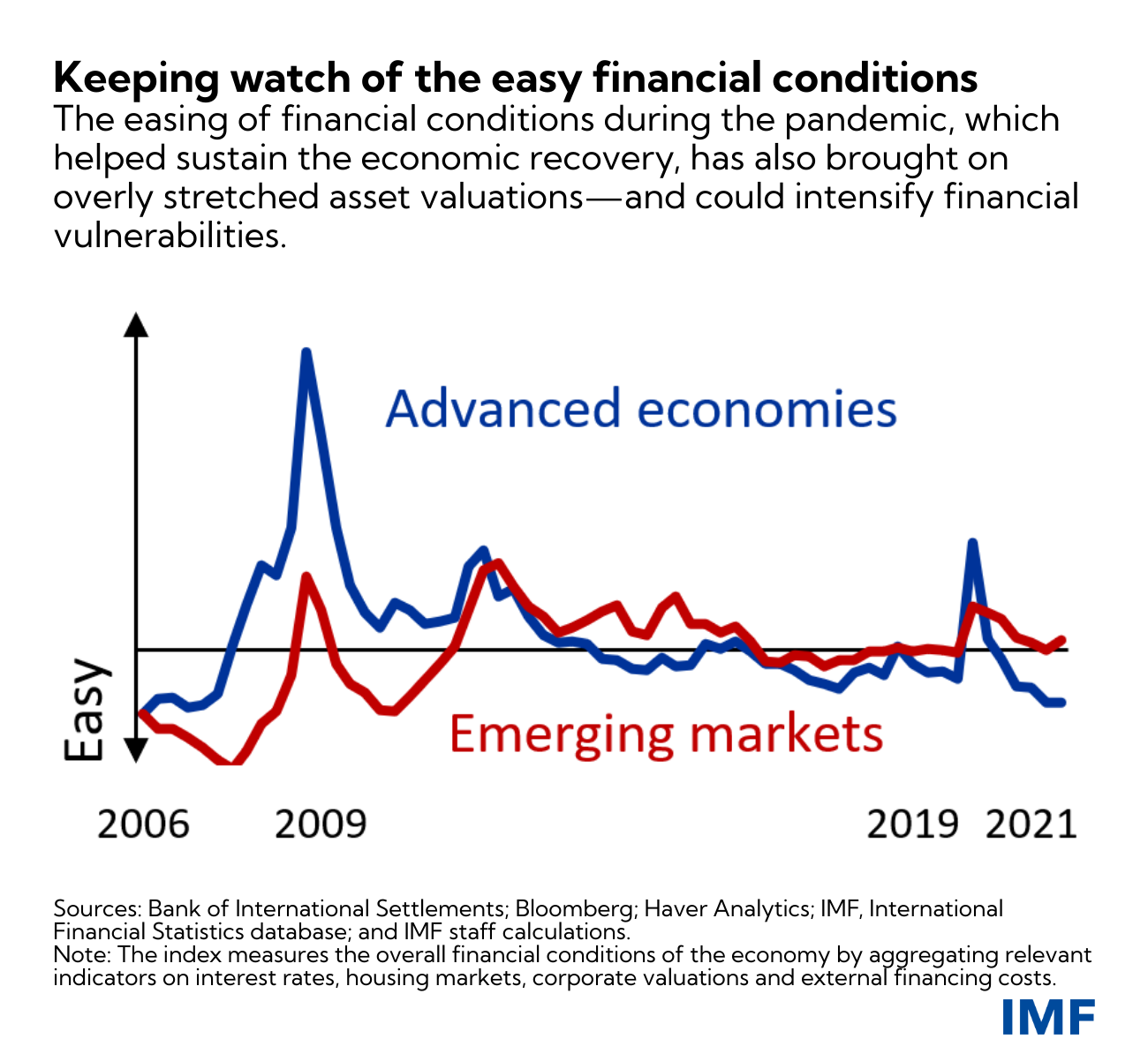
Amid still easy financial conditions overall, our analysis finds that financial vulnerabilities continue to be elevated in several sectors—but are masked, in part, by the massive policy stimulus. Policymakers are now confronted with a challenging trade-off: They must continue to provide near-term support to the global economy, even as they must simultaneously try to avoid the buildup of medium-term financial-stability risks. Managing this trade-off is a key challenge confronting policymakers.
A prolonged period of extremely easy financial conditions during the pandemic—which certainly has been needed to sustain the economic recovery—has allowed overly stretched asset valuations to persist. If that overstretch continues, it may, in turn, intensify financial vulnerabilities. Some warning signs—for example, increased financial risk-taking, as well as rising fragilities in the nonbank financial institutions sector—point to a deterioration in the underlying foundations of financial stability. If left unchecked, such vulnerabilities may persist into the longer term and become structural issues.
Policy action
Policymakers will need action plans that guard against unintended consequences. Monetary and fiscal policy support should be more targeted and tailored to country-specific circumstances, given the varying pace of the recovery across countries. Central banks will need to provide clear guidance about their future approach to monetary policy, aiming to avoid an unwarranted or abrupt tightening of financial conditions. Monetary authorities should remain vigilant, and if price pressures turn out to be more persistent than anticipated, act decisively to avoid an unmooring of inflation expectations. Fiscal support can appropriately shift toward more targeted measures and be tailored to country-specific characteristics.
Policymakers should take early action and tighten selected macroprudential tools to target pockets of elevated vulnerabilities. This is critical for addressing the potential unintended consequences of their unprecedented measures, given the possible need for prolonged policy support to ensure a sustainable recovery.
Policymakers in emerging and frontier markets should, where possible, begin to rebuild fiscal buffers and implement structural reforms. While facing several domestic challenges (higher inflation and fiscal concerns), some of those economies remain exposed to the risk of a sudden tightening in external financial conditions.
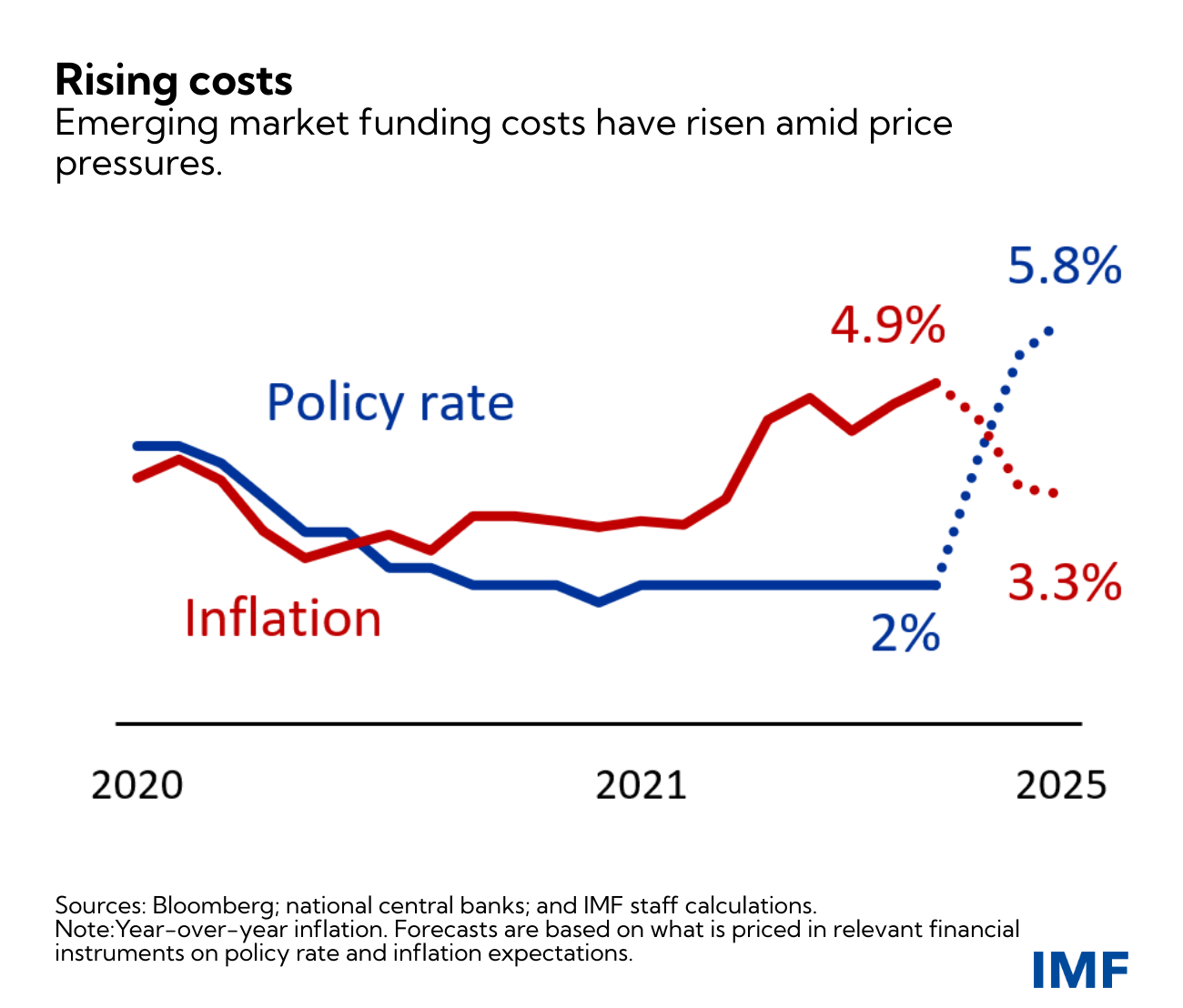
In a context of higher price pressures, investors are now pricing in a rapid and fairly sharp tightening cycle for many emerging markets, although the increase in inflation is expected to be temporary. Rebuilding buffers and implementing enduring reforms to boost economic growth prospects will be pivotal to protect against the risk of capital-flow reversals and an abrupt increase in financing costs.



